Polyvinyl Ester Resins
Properties and Applications
Vinyl ester resins are thermosetting resins that can be crosslinked through reaction of their vinyl groups. They are prepared by esterification of epoxy resins with unsaturated vinyl acids such as methacrylic acid. The resulting resins are then dissolved in reactive monomers.
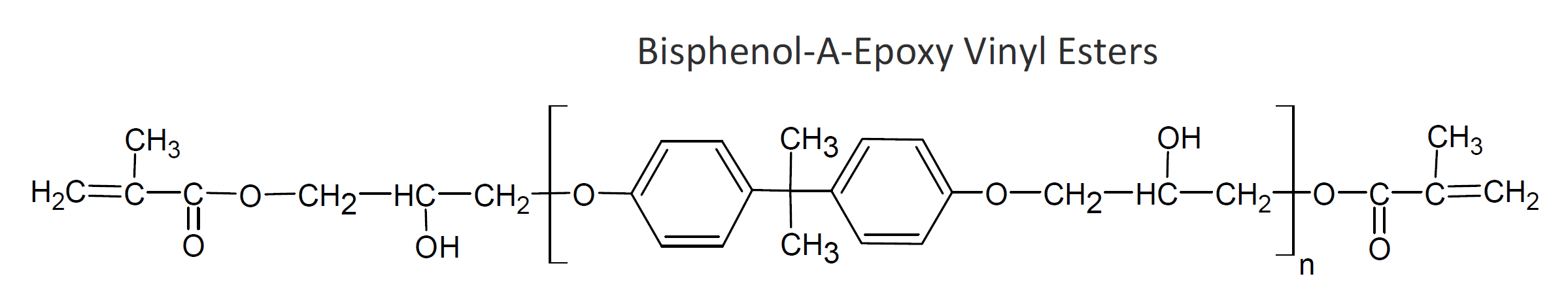
Vinyl ester resins are easy to process and their physical properties
in the uncured state are very similar to those of polyester resins. However, when crosslinked,
vinyl esters are noticeably stronger and tougher than conventional polyester resins.
They also have superior stress-fatigue and chemical resistance at both room and elevated temperature.
Vinyl ester resins are mainly used as matrix resins in glass,
carbon, or aramid fiber reinfoced plastics which they easily wet and bond to.
These composites are typically produced via filament winding, lamination,
or pultrusion. The largest use of vinyl ester resins is in chemical plants.
They are mainly used for corrosion resistant components and coatings
such as tanks, pipes and flue stack linings. They often bridge the gap between
conventional polyester resins and epoxies.